INDUSTRY IN RAJASTHAN
Rajasthan, traditionally known for its agrarian economy, is categorized as a backward state in terms of industrial development. The primary reasons for this underdevelopment are inadequate infrastructure and the state’s harsh climate. However, some cities like Kota have witnessed rapid industrial growth, earning it the title of the industrial city of Rajasthan. Rajasthan currently ranks 10th in India in terms of industrial presence.
At present, the major industrial hubs in Rajasthan include:
- Jaipur: The city with the highest number of industries and factories.
- Alwar: Notable for having the highest concentration of large industries.
Classification of Industries
Industries in Rajasthan can be classified based on several criteria:
- On the Basis of Size: Industries are categorized into three types based on capital investment and turnover.
- On the Basis of Manufacturing: Industries are grouped according to the type of raw material used and the products they manufacture.
- On the Basis of Ownership: This classification refers to whether industries are privately or publicly owned.
- On the Basis of Size
Industries in Rajasthan, based on size, can be divided into three categories: Micro, Small, and Medium. These categories are defined by the amount of capital invested and the turnover of each type:
| Industry Type | Capital/Investment | Turnover |
|---|---|---|
| Micro Industries | Less than ₹1 crore | Less than ₹5 crore |
| Small Industries | ₹1 crore to ₹10 crore | ₹5 crore to ₹50 crore |
| Medium Industries | ₹10 crore to ₹20 crore | ₹50 crore to ₹250 crore |
Additionally, Cottage Industries in Rajasthan consist of low-technology, home-based industries primarily aimed at self-sufficiency rather than profit.
- On the Basis of Manufacturing
Industries can also be categorized based on the raw materials used and the products they manufacture. These include:
| TYPE OF INDUSTRY | SUBCATEGORIES |
| Agriculture-Based Industry |
|
| Mineral-Based Industry | |
| Forest Produce-Based Industry | |
| Engineering or Technology-Based Industry | |
| Chemical Fertilizer Industry |
On the Basis of Ownership
Ownership is another criterion for classifying industries in Rajasthan. Industries are broadly divided into:
- Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs): These are government-owned and operate on a not-for-profit basis, contributing to social welfare and employment.
- Private Sector Enterprises: These industries are privately owned and focus on profitability, catering to both domestic and international markets.
AGRICULTURE-BASED INDUSTRY
Agriculture-based industries play a pivotal role in Rajasthan’s economy, leveraging the state’s agricultural resources to drive industrial growth. These industries use raw materials sourced from farming and livestock to produce a variety of products, contributing significantly to the livelihood of rural populations and the state’s overall development.
- The Cotton Textile Industry
The Cotton Textile Industry is one of the most prominent agricultural-based industries in Rajasthan. It has a rich historical background and plays a significant role in the state’s industrial economy.
- Raw Material: Cotton.
- The first cotton textile mill, The Krishna Cotton Mill, was established in 1889 in Biwar, Ajmer.
- The founders were Seth Damodar Das Rathi and Colonel Dixon.
The cotton textile industry has since expanded, with multiple prominent mills emerging across Rajasthan, such as:
| Mill | Year Established | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Edward Textile Mill | 1906 | Beawar |
| Mahalakshmi Textile Mill | 1925 | Beawar |
| Rajasthan Co-operative Spinning Mill | 1965 | Gulabpura (Bhilwara) |
| Gangapur Co-operative Spinning Mill | 1981 | Bhilwara |
| Sri Ganganagar Co-operative Spinning Mill | 1978 | Hanumangarh |
These mills are major contributors to the state’s cotton textile production and employ thousands of workers.
SPINFED: Rajasthan State Cooperative Spinning and Ginning Mills Federation Limited
Key Facts About SPINFED:
Bhilwara is often referred to as the Manchester of Rajasthan due to its strong textile production base. |
- Sugar Industry in Rajasthan
The sugar industry in Rajasthan primarily relies on sugarcane and beetroot as raw materials. Over the years, the state has developed a few key sugar mills, each with specific historical significance.
Major Sugar Mills in Rajasthan
| Name | Year Established | Location | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mewar Sugar Mill | 1932 | Chittorgarh | First Private Sugar Mill |
| Ganganagar Sugar Mill | 1937 | Sriganganagar | First Public Sugar Mill |
| Keshoipatan Sugar Mill | 1965 | Bundi | First Cooperative Sugar Mill |
| Udaipur Sugar Mill | 1976 | Udaipur | Public Sector |
Among these, Ganganagar Sugar Mill is noteworthy as the only operating sugar mill. It has diversified its operations into ventures such as:
- Country wine manufacturing.
- Manufacture of heritage liquor.
- Production of high-tech precision glass products at The Hi-Tech Precision Glass Factory in Dholpur.
This diversification highlights the adaptation of Rajasthan’s sugar industry to modern needs and technological advancements.
- Wool Industry in Rajasthan
Rajasthan ranks first in India in wool production, contributing 34.46% of the total production. The state has established a robust wool industry, centered around major cities and institutions.
Key Centers of the Wool Industry:
- Central Wool Board – Located in Jodhpur, it is the central body overseeing wool-related activities in the state.
- Wool Testing Laboratory – Situated in Bikaner, it ensures the quality and standards of wool products.
- State Wool Mill – Also in Bikaner, a hub of wool production.
- Central Sheep and Wool Research Center – Based in Avikanagar (Tonk), this center conducts research on wool production and sheep farming.
The wool market in Bikaner is one of the largest in India, making it a significant trade center for wool.
- Vegetable Ghee and Mustard Oil Industry
Rajasthan is also a key producer of vegetable ghee and mustard oil. The state’s first Vanaspati Ghee Factory was established in Bhilwara in 1964.
- The city of Jaipur holds the record for the highest production of both vegetable ghee and mustard oil in the state.
Major Mustard Oil Factories in Rajasthan:
- Chambal – Located in Jaipur.
- Veer Balak – Jaipur.
- Netaji – Jaipur.
- Engine Mark – Bharatpur.
These factories play a vital role in meeting the state’s demand for cooking oil and other related products.
- Dairy Industry
Rajasthan’s dairy industry has seen significant development, especially in Jaipur, which leads the state in dairy production. The state’s first dairy, named Padma, was established in Ajmer in 1938.
- The Rajasthan State Dairy Development Corporation was established in 1975 in Jaipur, in collaboration with the World Bank, marking a turning point in the state’s dairy sector.
The dairy sector in Rajasthan has evolved through a three-tier structure aimed at improving efficiency and streamlining milk production. This system is categorized as follows:
Three-Tier Structure for Dairy Development:
- Top Tier: Rajasthan Cooperative Dairy Federation (RCDF), established in 1977 in Jaipur.
- District Level: Various district milk cooperatives operate under the umbrella of RCDF.
- Village Level: Primary cooperative milk societies form the grassroots tier of the system.
Major Dairy Units Operating in Rajasthan
| Name | Location | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| WRMUL – Western Rajasthan Milk Union Ltd. | Jodhpur | – |
| URMUL – Uttari Rajasthan Milk Union Ltd. | Bikaner | – |
| Gangmul – Ganganagar Milk Union Ltd. | Ganganagar | – |
| Metro Dairy | Bassi (Jaipur) | 11 lakh liters |
| Camel Milk Marketing Center | Jaipur | 2100 liters/day |
The establishment of the camel milk marketing center in Jaipur, with a capacity of 2100 liters per day, highlights the state’s diversification in the dairy industry to include products such as camel milk, which is unique to Rajasthan.
- Biodiesel Industry in Rajasthan
Rajasthan has also made strides in the production of biodiesel, focusing on Ratanjot (Jatropha) and Karanj as raw materials.
- Biodiesel Refineries are primarily located in Kaldwas (Udaipur).
- The Biodiesel Plant at Jhamar Kotra (Udaipur) is an essential unit in biodiesel production, contributing to the state’s renewable energy initiatives.
- Olive Oil Industry in Rajasthan
The olive oil industry in Rajasthan has emerged as an innovative agro-based industry, primarily using olive as raw material. Key developments include:
- Olive Refinery: Located in Lunkaransar (Bikaner).
- An Olive Tea Plant has been established in Jaipur-Bassi, indicating diversification in the use of olives beyond oil production.
MINERAL-BASED INDUSTRIES IN RAJASTHAN
Rajasthan is rich in mineral resources and holds a prominent position in India for the extraction and processing of a wide variety of minerals. The state’s mineral-based industries play a significant role in its industrial development and contribute immensely to the national economy. Key mineral-based industries include cement, glass, salt, marble, granite, mica, and more.
- Cement Industry
- Rajasthan is one of the top producers of cement in India, with raw materials such as limestone, gypsum, and silica forming the basis of production.
- The state’s first cement factory was established between 1912-1913 by ACC (Associate Cement Company) in Lakheri (Bundi).
Major White Cement Factories:
- JK White Cement Factory – Gotan (Nagaur)
- JK White Cement Factory – Mangrol (Chittorgarh)
- Birla White Cement Factory – Kharia Khangar (Jodhpur)
Major Cement Production Units
| Factory Name | Location |
|---|---|
| JK Cement Factory | Nimbahera (Chittorgarh) |
| Ultratech Cement Factory | Chittorgarh |
| Chetak Cement Factory | Chittorgarh |
| Lafarge Cement Factory | Chittorgarh |
| Associate Cement Company | Lakheri (Bundi) |
| Bangar Cement Factory | Pali |
| Binani Cement Factory | Pindwara (Sirohi) |
| Shree Cement | Beawar (Ajmer) |
| Shri Ram Cement | Kota |
| Grasim Cement Factory | Kotputli (Jaipur) |
| Mangalam Cement Factory | Modak (Kota) |
| Jaipur Cement Factory | Sawai Madhopur |
- Glass Industry
The glass industry in Rajasthan is a key sector that capitalizes on the abundant silica sand and other necessary raw materials available in the state. The major hubs for glass production include Dholpur, Kota, and Alwar.
- The glass industry in Rajasthan relies heavily on raw materials such as silica sand, sodium sulphate, and saltpeter (a byproduct of the sugar industry).
- Dholpur is a major hub for glass development in Rajasthan.
- Salt Industry in Rajasthan
Rajasthan’s salt industry is centered around the state’s vast saltwater lakes, providing an essential resource for both domestic and industrial consumption.
Major Salt Production Units in Rajasthan:
- Sambhar Salt Limited – Located in Jaipur, this is one of the oldest and largest salt producers in the region.
- Pachpadra Salt Works – Based in Barmer, this facility plays a crucial role in Rajasthan’s salt production.
- Didwana Salt Works – Located in Nagaur, it is another significant player in the state’s salt industry.
These salt production units form the backbone of India’s salt economy, contributing significantly to the national production.
- Marble Industry in Rajasthan
Rajasthan holds the top spot in India for marble production, with the state known for its high-quality marble that is used for both domestic construction and export. The marble from Rajasthan is highly regarded for its durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Rajsamand: Known for its extensive marble production, the region has the highest number of processing units.
- Kishangarh (Ajmer): The largest marble market in India is located here, where domestic and international buyers procure high-grade marble.
- Makrana: Famous for producing white marble, Makrana marble is used in iconic monuments such as the Taj Mahal and is renowned worldwide for its quality.
- Granite Industry in Rajasthan
The granite industry in Rajasthan is another cornerstone of the state’s mining sector. Granite is extracted from regions such as Jalore, Barmer, and Sirohi.
- Jalore is known as the Granite City of Rajasthan, due to its significant granite reserves and production capabilities. The high-quality granite from this region is used both within India and in export markets.
- Mica Industry in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is also famous for its mica production, which is essential for the electronics and electrical industries. The key center for mica production is Bhilwara, where the Mica Brick Factory is located.
- Bhilwara is also called the Mica City because of its significant contributions to mica production, which is used in various electrical and industrial applications.
FOREST PRODUCE-BASED INDUSTRIES IN RAJASTHAN
These industries primarily deal with the extraction and processing of natural products from Rajasthan’s forests.
- Timber Industry: Timber is harvested sustainably from forest reserves and used in the construction and furniture industries.
- Gum Production: Chauhatan in Barmer is a major center for gum production, which is used in various industries.
- Silk and Sericulture: Udaipur has become a hub for silk production, with a focus on sustainable sericulture practices.
ENGINEERING OR TECHNICAL INDUSTRY IN RAJASTHAN
The engineering sector in Rajasthan is diverse, producing a wide range of industrial and consumer products. Below are some of the key industries and their respective products.
| Industry | Product | Location |
|---|---|---|
| National Engineering Company | Ball and Bearing | Jaipur |
| Jaipur Metals | Electricity Meters | Jaipur |
| Capstan Meter | Water Meter | Jaipur, Pali |
| Rajasthan Electronics Corporation | TV Sets | Jaipur |
| Mann Industries | Iron Door & Tower Construction | Jaipur |
| Cable Industries | Cables | Kota |
| Instrumentation | Equipment/Machinery | Kota |
| J & K Electronics | TV Sets | Kota |
| Florespar Plant | Iron Mixing Plant Construction | Dungarpur |
| CIMCO Wagon Factory (1957) | Railway Coaches | Bharatpur |
These industries cater to both domestic and international markets, producing goods ranging from everyday consumer electronics to specialized industrial machinery.
CHEMICAL FERTILIZER INDUSTRY IN RAJASTHAN
Rajasthan is also a key player in India’s chemical fertilizer industry. The state is home to several large-scale fertilizer plants that produce essential fertilizers for agriculture.
- Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals – Located in Gadepan (Kota), this plant produces a wide range of fertilizers used across India.
- National Chemicals and Fertilizers – Kapasan (Chittorgarh), specializes in the production of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP), one of the most commonly used fertilizers.
- Rajasthan State Chemical Works – Didwana (Nagaur), another critical unit contributing to the state’s chemical fertilizer production.
INDUSTRIAL CLASSIFICATION BASED ON OWNERSHIP
Industries can be classified based on their ownership into three broad categories: private sector industries, public sector industries, and joint sector or cooperative industries. The classification reflects who owns, manages, and controls the industrial operations. This classification helps in understanding the structure, goals, and operations of industries, which differ based on whether they are privately owned, government-owned, or a combination of both.
Industries in Rajasthan can also be classified based on ownership:
- Private Sector Industries
Private sector industries are owned, controlled, and managed by private individuals, companies, or corporations. The primary goal of these industries is to make a profit. Private sector industries operate in a competitive environment and are accountable to their shareholders or owners.
Key Features of Private Sector Industries:
- Ownership: Owned by private individuals or corporations.
- Objective: Profit maximization.
- Control and Management: Managed by private entrepreneurs, boards, or owners.
- Funding: Financed by private capital, shareholders, or bank loans.
- Examples:
- Reliance Industries (Oil, Petrochemicals)
- Tata Steel (Steel Manufacturing)
- Infosys (IT and Consulting)
- Aditya Birla Group (Cement, Textile, and Financial Services)
In Rajasthan, private sector industries include cement manufacturing, textiles, gems and jewelry, and tourism. Cities like Jaipur and Bhilwara are known for their textile industries, which are largely privately owned.
- Public Sector Industries
Public sector industries are owned, operated, and controlled by the government. These industries are often established to serve public welfare and ensure that critical sectors like defense, energy, and infrastructure are well-developed, even if they are not as profitable as private sector industries.
Key Features of Public Sector Industries:
- Ownership: Owned by the central or state government.
- Objective: Public welfare, infrastructure development, and equitable economic growth.
- Control and Management: Managed by government-appointed officials.
- Funding: Financed through government budgets, bonds, and public funding.
- Examples:
- Steel Authority of India (SAIL) (Steel Production)
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) (Energy)
- BHEL (Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited) (Power Equipment)
- Hindustan Zinc Limited (Zinc Mining in Rajasthan)
In Rajasthan, some important public sector industries include:
- Hindustan Zinc Limited in Udaipur.
- Rajasthan State Mines and Minerals Limited (RSMM) in Udaipur.
- Rajasthan Electronics and Instruments Limited (REIL) in Jaipur.
These industries focus on mining, minerals, and heavy machinery production and serve critical needs in the state and the country.
- Cooperative or Joint Sector Industries
Cooperative industries are owned and operated by a group of individuals or entities who come together with a common goal. The joint ownership may include both private individuals and government agencies. In joint sector industries, the government and private sector work together in partnership. The focus of these industries is not solely profit-making but also ensuring that certain sectors or communities benefit equally from the industry.
Key Features of Cooperative and Joint Sector Industries:
- Ownership: Owned and operated by both the government and private individuals or organizations, or collectively by the community.
- Objective: Balance between profit and welfare; promoting shared ownership and community benefits.
- Control and Management: Managed jointly by representatives from both public and private sectors, or by cooperatives formed by individuals.
- Funding: Financed through contributions from both private and government sectors or cooperative members.
- Examples:
- Amul (Cooperative Dairy Sector)
- IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited) (Fertilizer Production)
- Rajasthan Cooperative Spinning Mills (Textile Production)
In Rajasthan, SPINFED (Rajasthan State Cooperative Spinning and Ginning Mills Federation Limited) is a major example of a cooperative industry. It includes all three cooperative cotton textile mills and provides employment and income to large groups of workers, especially in rural areas. Another important example is the Rajasthan State Cooperative Dairy Federation (RCDF), which promotes milk production and dairy development through cooperatives.
Comparison of Ownership Types
| Ownership Type | Ownership | Management | Objective | Funding | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private Sector | Private Individuals or Corporations | Private Entrepreneurs or Boards | Profit Maximization | Private Capital, Shareholders | Reliance, Tata, Aditya Birla |
| Public Sector | Central or State Government | Government Officials | Public Welfare, Infrastructure | Government Budgets, Public Funds | ONGC, SAIL, Hindustan Zinc |
| Cooperative Sector | Community or Joint Ownership | Elected Representatives or Joint Management | Welfare, Profit Sharing | Contributions from Members, Government | Amul, IFFCO, Rajasthan Cooperative Spinning Mills |
Public Enterprises in Rajasthan
Rajasthan has a well-defined structure for public enterprises, divided into two categories:
- Central Government Undertakings
- State Government Undertakings
These public enterprises are significant contributors to the state’s industrial growth and include major sectors such as mining, manufacturing, and infrastructure.
Structure of Public Enterprises in Rajasthan
| Type of Undertaking | Number of Undertakings |
|---|---|
| Central Government Undertakings | 7 |
State Government Undertakings
|
23
6 17 |
Central Government Undertakings/Industries (7)
These central government undertakings form the core of Rajasthan’s public sector industries, covering a wide range of sectors from metal mining to pharmaceuticals.
Statutory Boards in Rajasthan (6)
| Year | Board |
|---|---|
| 1955 | Rajasthan Finance Corporation |
| 1957 | Agricultural Warehousing Corporation |
| 1964 | Rajasthan State Road Transport Corporation (RSRTC) |
| 1970 | Rajasthan Housing Board Corporation (RHB) |
| 1974 | State Agricultural Marketing Board |
| 1975 | State Land Development Corporation |
These statutory boards are essential in managing the financial and infrastructural aspects of Rajasthan’s economy, with the Rajasthan Finance Corporation being a notable financial institution supporting industrial growth.
Companies Under the Companies Act (17)
Some of the key undertakings governed by the Companies Act of Rajasthan include:
- Raj State Mines & Minerals Ltd. (1974) – Located in Udaipur, this company is crucial in mining and mineral processing.
- State Electricity Distribution Corporation – Jodhpur, Ajmer, Jaipur.
- REIL (Rajasthan Electronics & Instruments Ltd.) – Based in Kanpur and Jaipur, REIL is involved in the production of various electronic and instrumentation products.
Industrial Development Efforts in Rajasthan
Rajasthan has undertaken several initiatives to boost industrial development through structured policies and programs aimed at enhancing investment, creating special economic zones, and establishing industrial parks.
Key Efforts:
- Industrial Policies
The latest industrial policy was issued on 1st July 2019. This policy is focused on creating a favorable business environment by simplifying regulations, providing fiscal incentives, and encouraging Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). Notably, the MSME policy was introduced on 20th November 2015.
Rajasthan has issued several key industrial policies over the years to support the growth of its industries. These include:
- 1978 Industrial Policy: The first industrial policy aimed at creating a strong industrial base.
- 1991 Industrial Policy: Focused on liberalization and privatization.
- 1994 Industrial Policy: Introduced reforms to boost private sector participation.
- 1998 Industrial Policy: Aimed at modernizing industries and fostering technological advancements.
- 2010 Industrial Policy: Focused on sustainable development and industrial infrastructure.
- 2019 Industrial Policy: The most recent policy, aimed at further enhancing Rajasthan’s industrial competitiveness.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in Rajasthan
The SEZ program in Rajasthan is managed by RIICO (Rajasthan State Industrial Development and Investment Corporation), and it aims to boost economic activities through various sector-specific zones. These SEZs are designed to attract investments and promote exports, focusing on specific industries.
Major SEZs in Rajasthan
| SEZ | Related Area | Status | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boranada SEZ | Guargum, Handicrafts | Active | Jodhpur |
| Sitapura SEZ | Gems & Jewellery | Active | Jaipur |
| Mahindra SEZ | IT, Handicrafts | Active | Jaipur (Kalwara) |
| Somani SEZ | Hardware, Software | Active | Alwar |
| RNB SEZ | Textile | Active | Bikaner |
| Vatika SEZ | Information Technology (IT) | Proposed | Jaipur |
These SEZs are tailored to promote specific industries, such as textiles, IT, gems & jewellery, and handicrafts, leveraging Rajasthan’s rich cultural heritage and skilled labor.
- Industrial Parks and Complexes in Rajasthan
Rajasthan has a well-structured network of industrial parks and complexes aimed at developing specific industries, promoting local entrepreneurship, and attracting foreign investment.
Key Industrial Parks and Complexes in Rajasthan
| Park | Location | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Japanese Park (JETRO) | Neemrana, Alwar | Collaboration with Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO) |
| Korean Park (GWJT) | Ghilot, Alwar | Established in Alwar to promote Korean industrial units |
| Ceramic Zone | Ghilot | Focus on ceramic production |
| Agro Food Park | Sri Ganganagar, Jodhpur, Kota, Alwar | Agro-processing and food industries |
| Mega Food Park | Roopangarh, Ajmer | Agro-processing center with large-scale food production |
| Information Technology (IT) Park | Jaipur, Kota, Udaipur | IT development zones for software and hardware companies |
| Garment/Apparel Park | Jagatpura (Mahal Road), Jaipur | Focus on garment manufacturing and apparel industries |
| Stone Park | Mandore, Jodhpur; Masalpur, Karauli | Industrial area for stone processing and trade |
| Software Park (REIL) | Kanakapura, Jaipur | Rajasthan Electronics Instrument Ltd. Software Park |
| Wool Complex | Khara (Bikaner), Ajmer | Wool production and processing hubs |
| Export Promotion Industrial Park | Sitapura (Jaipur), Boranada (Jodhpur), Neemrana (Alwar) | Export-oriented industrial zones |
- Industrial Investment Program in Rajasthan
The Industrial Investment Program in Rajasthan is a comprehensive set of initiatives launched by the state government to promote industrial growth, attract investments, and enhance infrastructure for businesses. The state has undertaken multiple efforts to make it a more attractive destination for domestic and international investors. The cornerstone of this investment strategy is the Resurgent Rajasthan Summit, alongside other policies aimed at fostering innovation, providing incentives, and easing regulatory frameworks for industries.
Resurgent Rajasthan Partnership Summit
The Resurgent Rajasthan Summit is a biennial event aimed at attracting large-scale investments to the state. It was first held in 2008, and subsequent summits have focused on creating a collaborative platform for investors, entrepreneurs, and policymakers.
Key Highlights:
- Investment Announcements: The 2015 Resurgent Rajasthan Summit witnessed ₹3.3 lakh crore worth of investment proposals, with significant attention on renewable energy, manufacturing, and IT sectors.
- Key Sectors: Focus sectors include solar energy, defense manufacturing, auto components, tourism, mining, and IT services.
- International Participation: The summit has seen participation from international delegations, especially from countries like Japan, South Korea, Germany, and France.
The summit creates opportunities for public-private partnerships (PPP) and encourages foreign direct investment (FDI) in sectors like infrastructure, logistics, and education.
Resurgent Rajasthan (MSME Policy)
In alignment with the Resurgent Rajasthan Program, the MSME Policy (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) was implemented on 20 November 2015. The policy focuses on encouraging small enterprises to thrive by providing fiscal incentives, easy regulations, and better access to infrastructure.
This program was instrumental in attracting large-scale investments, particularly in renewable energy sectors such as solar power.
- Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC)
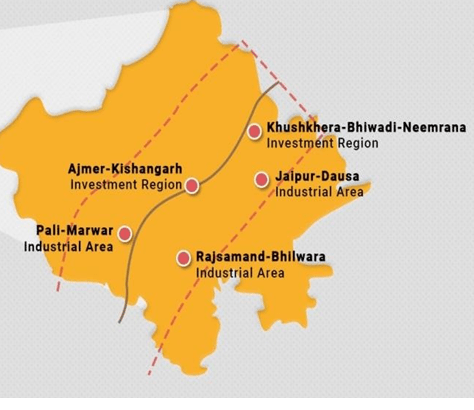
The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) is one of the most significant industrial projects undertaken by the Indian government, with technical and economic cooperation from Japan. This project is designed to connect Noida (New Delhi) to Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Mumbai, Maharashtra), covering a total length of 1483 km, out of which 558 km passes through Rajasthan.
Key Features of DMIC in Rajasthan:
- 7 districts of Rajasthan are included in the core of the industrial corridor, while 22 districts have been identified within its area of influence.
- The project includes 24 industrial areas and 8 industrial investment zones, five of which are located in Rajasthan.
- Rajasthan’s involvement will help boost industrial activity in the state, connecting it with the larger industrial ecosystem along the DMIC route.
Major Nodes in Rajasthan Along the DMIC
| Node No. | Location | Area |
|---|---|---|
| Node No. 7 | Alwar – Khushkhera, Bhiwadi, Neemrana | Investment Area |
| Node No. 8 | Jaipur – Dausa | Industrial Area |
| Node No. 9 | Ajmer-Kishangarh | Investment Zone |
| Node No. 10 | Rajsamand – Bhilwara | Industrial Area |
| Node No. 11 | Pali-Marwar | Industrial Area |
This project will significantly enhance Rajasthan’s role in India’s industrial network by creating investment zones and industrial areas that encourage manufacturing, logistics, and infrastructure development.
Industrial Institutes in Rajasthan
Rajasthan has established several key industrial institutes that aim to facilitate the growth of industries, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs). These institutes provide essential services such as financial assistance, infrastructure development, and support to industries in rural and tribal areas.
- RFC (Rajasthan Financial Corporation)
- Established: January 1955
- Headquarters: Jaipur
Objective: RFC provides short-term loans to Micro, Small, and Medium Industries (MSMEs) with a loan amount ranging from ₹2000 to ₹20 crores. The primary goal of RFC is to offer financial support at affordable rates to promote the growth of small industries in Rajasthan.
Schemes Offered by RFC:
- Flexi Loan Scheme: Provides loans to MSMEs at affordable rates.
- Top-Up Scheme: Offers additional funding to small-scale industries for technical and machinery development.
- SEMFEX Scheme (Self-Employed for Ex-Servicemen Scheme): Supports ex-servicemen in setting up industries by providing financial assistance.
- RAJSICO (Rajasthan Small Industries Corporation Limited)
- Established: June 1961
- Headquarters: Jaipur
Objective: RAJSICO focuses on developing small industries, particularly in tribal areas. It provides raw materials, machinery, and technical facilities to small-scale industries across the state. Additionally, it helps in marketing goods produced by small industries, ensuring that local businesses have access to larger markets.
- RIICO (Rajasthan State Industrial Development and Investment Corporation Limited)
- Established: 1969 (Reorganized in 1980)
- Headquarters: Jaipur
Objectives:
- To provide long-term loans to small, medium, and large-scale industries.
- To allocate land for industrial development across Rajasthan.
- RIICO serves as the apex body for industrial development in Rajasthan, playing a pivotal role in facilitating industrial growth by offering financial and infrastructural support to a wide range of industries.
- RUDA (Rural Non-Farm / Agriculture Development Agency)
- Established: 1995
- Headquarters: Jaipur
Objectives:
- Training and skill development in non-agriculture sectors, especially for rural populations.
- RUDA focuses on training for wool and textile industries, leather industries, and minor minerals sectors. The agency plays a significant role in enhancing the capacity of rural industries, contributing to employment generation and sustainable development in non-farm sectors.
INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT SCHEMES IN RAJASTHAN
Rajasthan has launched various industrial development schemes aimed at promoting entrepreneurship, enhancing industrial growth, and supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These schemes provide financial assistance, incentives, and regulatory support to encourage the establishment and growth of industries across the state. Below are the key industrial development schemes initiated by the government of Rajasthan.
- Mukhya Mantri Swavalamban Yojana
- Launched: 2013
- Objective: To promote self-employment by providing loans of up to ₹10 lakhs to hand-based artisans, small entrepreneurs, and individuals looking to set up their own businesses.
Key Features:
- Encourages small-scale industries and handicraft sectors.
- Focuses on rural and semi-urban entrepreneurs.
- Provides financial assistance and support for setting up small enterprises.
This scheme helps artisans and small business owners by offering easy access to credit, encouraging industrialization at the grassroots level.
- Mukhya Mantri Yuva Udyamita Protsahan Abhiyan
- Launched: 2013
- Objective: To provide financial support and loans to young entrepreneurs (aged 18-45) for setting up new industries.
Key Features:
- Loan amount ranges from ₹2.5 lakhs to ₹5 crores.
- Eligibility: The scheme targets individuals who have completed 10th grade, ITI, or are graduates.
- Encourages youth entrepreneurship in industries such as manufacturing, services, and agro-based sectors.
This scheme supports youth who want to enter the industrial sector by providing financial backing, technical support, and resources to establish businesses.
- Start-up Scheme
- Launched: 9th October 2015
- Objective: To provide financial support to entrepreneurs starting new businesses, particularly in innovative sectors such as technology, services, and manufacturing.
Key Features:
- Rajasthan is the fifth state to adopt this scheme after Karnataka, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- Focuses on fostering an ecosystem for start-ups by providing venture capital, incubation, and mentoring support.
- Helps entrepreneurs with the setup of industrial plans through government aid.
The Start-up Scheme seeks to make Rajasthan a hub for innovation by supporting entrepreneurs and start-ups that work on new technologies or disruptive business models.
- ASIDE Scheme (Assistance to States for Developing Export Infrastructure and Allied Activities)
- Launched: March 2002
- Objective: To promote industrial exports by developing export-oriented infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Supports the development of Export Promotion Industrial Parks (EPIPs) and Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
- Funds the creation of export infrastructure, including roadways, ports, and logistics hubs.
- Provides assistance for the development of warehousing, cold storage, and other facilities that support the export of industrial goods.
The ASIDE scheme ensures that Rajasthan’s export sector remains competitive by providing the necessary infrastructure and logistical support.
- Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme (RIPS)
- Objective: To provide tax and financial incentives to investors setting up industries in Rajasthan.
Key Features:
- Subsidies on electricity, stamp duty, and land conversion charges.
- Interest subsidies on loans taken for establishing industries.
- Exemption from VAT (Value Added Tax), CST (Central Sales Tax), and other state-level taxes for eligible industries.
RIPS is aimed at creating a conducive environment for large-scale industrial investments, helping Rajasthan become a more attractive destination for industries.
- Rajasthan MSME Policy
- Launched: 2015
- Objective: To promote Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the state.
Key Features:
- Financial assistance to MSMEs in the form of loans, subsidies, and credit facilities.
- Support for skill development, training, and technical assistance to help MSMEs grow.
- Focus on improving the ease of doing business for small-scale industries by simplifying regulations and processes.
The MSME sector forms the backbone of Rajasthan’s industrial landscape, and this policy focuses on strengthening it through financial support and capacity building.
- Single Window Clearance System (SWCS)
- Launched: 2011 (Revised in 2020)
- Objective: To provide a single-window clearance for all industrial project approvals, ensuring time-bound processing and minimizing bureaucratic delays.
Key Features:
- Online portal for real-time tracking of approval processes.
- Reduces the need for investors to approach multiple government departments.
- Provides faster approvals for land acquisition, environmental clearances, electricity connections, and other licenses.
SWCS makes it easier for industries to set up in Rajasthan by streamlining the approval process, improving the ease of doing business.
- Chief Minister’s Rajasthan Industrial Development Policy (2019)
- Objective: To promote industrial development by providing incentives for new industries, expansion projects, and technology adoption.
Key Features:
- Focus on promoting sustainable development through renewable energy industries, green manufacturing, and eco-friendly technologies.
- Support for the establishment of research and development (R&D) centers.
- Encourages women entrepreneurs by providing additional financial support for women-led businesses.
This policy is aligned with India’s goal of boosting industrial output while ensuring environmental sustainability and inclusive growth.
- E-Governance and IT Policy
- Launched: November 2015
- Objective: To promote e-governance in industrial operations, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and accountability.
Key Features:
- Focus on digitization of industrial records, applications, and clearances.
- Online portals for industrial license applications, land acquisition requests, and tax filings.
- Aimed at promoting IT services and software industries within Rajasthan.
This policy encourages the growth of the IT sector while ensuring that the governance of industries is efficient and technology-driven.
- Scheme for Revival of Sick Industries
- Objective: To revive sick industries that are on the verge of closure by providing them with financial assistance and restructuring support.
Key Features:
- Special packages and restructuring plans for debt-ridden industries.
- Interest subsidies on loans to help sick industries recover.
- Focus on employment retention and sustainability of critical industries in Rajasthan.
This scheme ensures that industries that face financial difficulties are given a second chance to restructure and become profitable again.
- District Industries Centers (DICs)
- Objective: To support industrial development at the district level by providing necessary clearances and incentives for setting up industries.
Key Features:
- Rajasthan has 36 District Industries Centers and 8 sub-centers.
- These centers assist with land acquisition, licensing, and technical support for small and medium industries.
- They also provide market information and support for export promotion.
DICs play a crucial role in decentralizing industrial development and ensuring that all districts in Rajasthan can benefit from industrialization.
- Industrial Corridor Projects
- Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC): Rajasthan is a key part of the DMIC, which spans 1483 km, with 558 km in Rajasthan. It includes investment regions such as Alwar, Jaipur, Ajmer, Rajsamand, and Pali.
- The state also participates in other industrial corridors that ensure connectivity, infrastructure development, and logistics improvements.
Rajasthan’s various industrial development schemes reflect the state’s commitment to fostering industrial growth, entrepreneurship, and innovation. Through these schemes, Rajasthan aims to attract investments, provide financial support to industries, and create a conducive environment for the MSME sector and large-scale industries alike. These initiatives play a crucial role in making Rajasthan an attractive destination for both domestic and foreign investors, contributing to its industrialization and economic growth.
Additional Points Related to Industrial Development
- District Level Industrial Centers: Rajasthan has 36 District Industries Centers and 8 sub-stations, playing a crucial role in facilitating industrial development at the district level.
- Single Window Clearance Act: Introduced in 2011 and revised in 2020, this act simplifies the process of establishing industries by offering a single-window clearance mechanism for all necessary approvals.
- E-Governance and IT Policy: Launched in November 2015, this policy ensures transparency and efficiency in industrial operations and governance, especially in IT-related industries.
Special Industrial Institutes of Rajasthan
Rajasthan has also established a range of institutes dedicated to research, training, and development for specific industries:
- Computer Aided Carpet Design Center – Jaipur
- Computer Aided Textile Design Center – Bhilwara
- Brahmaputra Research and Development Institute – Jodhpur
- Footwear Design Center – Mandore (Jodhpur)
- NIFT (National Institute of Fashion Technology) – Jodhpur
- Ceramic Research and Development Center – Bikaner
These institutes focus on providing specialized training and resources to industries like carpet and textile design, footwear manufacturing, and ceramics, ensuring that Rajasthan remains at the forefront of these sectors.
Rajasthan’s industrial landscape is shaped by well-structured support from institutions like RIICO and RUDA, which provide financial assistance, land, and training for industrial development. Coupled with targeted schemes like Mukhya Mantri Swavalamban Yojana and the Start-up Scheme, Rajasthan ensures that entrepreneurs, artisans, and industries have access to the necessary resources and financial support. The creation of special industrial institutes further strengthens the state’s industrial foundation, allowing it to maintain its leadership in sectors such as textiles, carpets, and ceramics.


