LIVESTOCK IN RAJASTHAN
LIVESTOCK CENSUS IN RAJASTHAN
The Livestock Census in Rajasthan is a critical activity managed by the Revenue Board in Ajmer. Conducted every five years, this census tracks the population and distribution of livestock in the state. The first livestock census took place in 1919-20, while the latest census, which is the 20th in the series, was conducted in 2019-20.
- First Census: 1919-20
- Latest Census: 2019-20 (20th Census)
In the 20th Livestock Census, the total livestock population was recorded at 567.75 lakhs, showing a slight decrease of 1.61% from the previous census (577 lakhs in 2012).
Animal Husbandry in the 20th Census
Animal husbandry forms a vital part of the rural economy in Rajasthan. According to the latest census data, the distribution of animals shows clear regional trends. Barmer, Jodhpur, Jaipur, and Udaipur districts lead in livestock population, while Dholpur, Kota, Sawai Madhopur, and Baran are at the lower end of the spectrum.
- Maximum Animal Husbandry: Barmer, Jodhpur, Jaipur, Udaipur
- Minimum Animal Husbandry: Dholpur, Kota, Sawai Madhopur, Baran
A map of Rajasthan with key regions for different livestock types such as Horse, Cow, Mule, Buffalo, Pig, Sheep, Goat, and Donkey can be seen in Figure 1 below. This map provides a visual representation of the concentration of specific types of livestock across different districts.
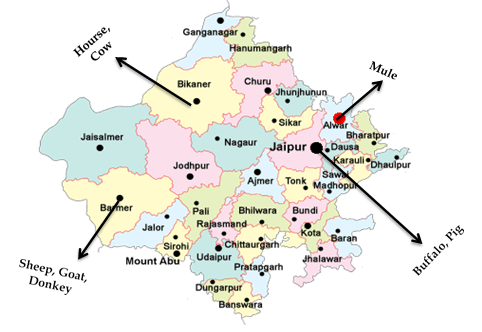
Livestock Distribution in Rajasthan (20th Census)
The data shows that different types of livestock dominate in various parts of the state. For instance:
- Mule and Buffalo/Pig: Concentrated in eastern parts, including Bharatpur and Dholpur.
- Horse, Cow, and Sheep/Goat/Donkey: Prevalent in the central and western parts, such as Barmer, Jaisalmer, and Bikaner.
Rajasthan’s Share in India’s Livestock Population
Rajasthan holds a significant share of the total livestock population in India, contributing 10.60% to the national livestock count. This makes the state a critical region in India’s animal husbandry and livestock economy.
Livestock Composition
The census provides detailed insights into the animal types that are most prevalent in Rajasthan:
- Goat: 36.70%
- Cow: 24.50%
- Buffalo: 24.11%
- Sheep: 13.92%
This distribution highlights Rajasthan’s role as a leading state in the production of goats and cows, which are vital for the dairy and meat industries.
Specialty in Livestock
Rajasthan leads India in the population of camels, donkeys, and goats, indicating the state’s unique livestock heritage and its adaptation to arid and semi-arid conditions. The following table summarizes the livestock that Rajasthan leads in:
| Rajasthan’s Leading Livestock – Camel, Donkey and Goat. |
Livestock Density and Regional Variations
The Livestock Density in Rajasthan, according to the 20th Livestock Census, stands at 166 animals per square kilometer. However, there are significant variations between districts. The following table illustrates the regions with maximum and minimum livestock density (in million):
Livestock Density in Rajasthan (20th Census)
| Maximum Density | Number | Minimum Density | Number |
| Dungarpur
Banswara Dausa Jaipur |
433
386 308 208 |
Jaisalmer
Bikaner Baran Churu |
62
90 110 117 |
Livestock Growth and Decline in Rajasthan
Highest Growth in Livestock Population
According to the 20th Livestock Census, the animals that experienced the highest growth in population are:
- Buffalo: 5.53% growth
- Cattle: 4.41% growth
The increase in buffalo and cattle populations is reflective of the growing demand for dairy products in the state, contributing to the state’s milk production economy.
Greatest Decline in Livestock Population
Conversely, some animals have experienced a significant reduction in population. The Donkey population has declined by 71.31%, followed by Mule (-60.33%), Pigs (-34.87%), Camel (-34.69%), and Sheep (-12.95%).
This trend shows a sharp decrease in certain animals, particularly those that are not directly linked to high-demand industries like dairy or meat production.
Population Decline in Livestock (20th Census)
| Animal | % Decline |
| Donkey | 71.31% |
| Mule | 60.33% |
| Pigs | 34.87% |
| Camel | 34.69% |
| Sheep | 12.95% |
Breeds of Livestock in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is home to a diverse variety of livestock breeds, particularly in goats, which are crucial for meat and milk production.
Goat Breeds in Rajasthan
Goats hold significant importance in Rajasthan’s rural economy. The region is home to several goat breeds, each adapted to local conditions and bred for specific purposes such as meat or milk production.
- Marwari and Lohi: Primarily found in North-West Rajasthan, these breeds are well known for their meat production. Marwari and Lohi goats are resilient and well-suited to the arid climate of western Rajasthan.
- Jhakhrana/Alwari: Native to Alwar district, this is the highest milk-producing goat breed in the region, making it an invaluable asset for the dairy industry in Rajasthan.
- Shekhawati: This breed, found in Sikar and Jhunjhunu, is unique as it is a hornless breed, developed by CAZARI (Central Arid Zone Research Institute) scientists. The Shekhawati breed is highly resilient and well adapted to semi-arid conditions.
- Parbatsari: Predominantly raised in Nagaur, Ajmer, and Tonk districts, this breed is known for producing high-quality milk.
- Barbari: Found in Eastern Rajasthan, Barbari goats are considered one of the most aesthetic breeds, often bred for their beauty as well as their productivity.
- Sirohi: Originating from Sirohi and Jalore districts, this breed is famous for its meat production. It is highly valued for its hardiness and adaptability.
- Jamanapari: Hailing from the Hadoti region, the Jamanapari breed is known for both meat and milk production, making it a dual-purpose breed that is widely raised for various benefits.
| Note: The Goats of Varun village in Nagaur are considered to be among the best breeds, known for their superior quality and productivity. |
A map of Rajasthan, shown below, marks the geographic distribution of these goat breeds, highlighting where each breed thrives.
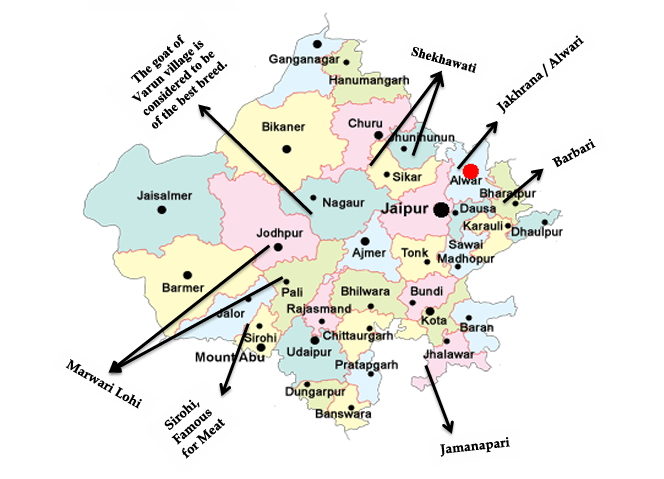
Cow Breeds in Rajasthan
Rajasthan also boasts a diverse population of cows, particularly in Bikaner and Jodhpur, which are known for their maximum cow populations. Some key cow breeds found in Rajasthan are listed below:
- Rathi: Predominantly found in Bikaner, Shri Ganganagar, and Jaisalmer, the Rathi cow is renowned for its high milk production, earning it the nickname “Kamdhenu of Rajasthan.”
- Tharparkar: This breed is native to Jaisalmer and Barmer districts, as well as parts of Sindh in Pakistan. It is a dual-purpose breed, used for both milk production and agricultural work, making it indispensable in rural Rajasthan.
- Gir: Native to Ajmer, Bhilwara, and Chittorgarh, the Gir breed originated from Gujarat. It is widely recognized for its hardiness and milk production capacity.
- Nagauri: Indigenous to Nagaur, this breed is known for its ability to carry heavy loads and is also useful for agriculture purposes.
- Kankrej: This breed, originating from Gujarat, is found in Barmer and Jalore. It is primarily raised for agricultural work and is capable of running long distances with loads.
- Mewati: Raised in Alwar and Bharatpur, the Mewati breed is used mainly for carrying loads.
- Hariyani: Found in Sikar and Jhunjhunu, this breed has its origins in Haryana.
- Malvi: This breed, native to Southern-Eastern Rajasthan, has its origin in Malwa (Madhya Pradesh) and is known for its strength and durability.
- Sanchori: Found in Jalore and Sirohi, the Sanchori breed is another important breed in the region, contributing to both milk production and agricultural labor.
Foreign Cow Breeds Introduced in Rajasthan
In addition to indigenous breeds, several foreign cow breeds have also been introduced in Rajasthan to improve milk production and resilience. Notable foreign breeds include:
- Jersey: Originating from America, the Jersey cow is widely known for its high milk yield.
- Redden: Hailing from Denmark, this breed is also known for its milk production capabilities.
- Holstein: Found in Holland and America, Holstein cows are recognizable due to their black and white spots. They are one of the highest milk-producing breeds, making them a popular choice for dairy farmers in Rajasthan.
Buffalo Breeds in Rajasthan
Buffaloes form an integral part of the livestock economy in Rajasthan, with Jaipur holding the maximum buffalo population. The following are some of the prominent buffalo breeds found in the state:
- Murrah (Khundi): Predominantly found in Eastern Rajasthan, the Murrah buffalo is known for being the highest milk-producing buffalo breed in the region. Its superior genetic traits make it a prized asset for dairy farming.
- Surti: Native to Udaipur, the Surti breed originates from Gujarat and is known for its adaptability to Rajasthan’s semi-arid conditions.
- Jafarabadi: Found in Southern Western Rajasthan, this breed is also of Gujarat origin and is raised primarily for milk production.
- Mehsana: Another buffalo breed from Southern Western Rajasthan, the Mehsana buffalo hails from Gujarat and is widely bred for its high milk yield.
- Bhadawari: Found in Eastern Rajasthan, the Bhadawari buffalo originates from Uttar Pradesh and is raised for its adaptability and milk production.
Sheep Breeds in Rajasthan
Sheep play a critical role in the economy of Rajasthan, especially in the districts of Barmer and Bikaner, which have the maximum sheep populations. Sheep are primarily raised for their wool, which is used in the production of textiles like rugs and blankets, and for their meat in some regions.
Prominent Sheep Breeds in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is home to several prominent breeds of sheep, each known for unique characteristics such as wool quality, adaptability, and region of origin.
- Malpuri: Found in the districts of Jaipur, Tonk, and Sawai Madhopur, the Malpuri breed is valued for its thick wool, which is commonly used to manufacture rugs and blankets.
- Chokla: Primarily found in Jhunjhunu, Sikar, and Bikaner, the Chokla breed is renowned for its high-quality wool. It is also known as the “Indian Merino”, given its superior wool quality that is often compared to the globally recognized Merino sheep.
- Sonadi/Chanothar: Native to Udaipur, Dungarpur, and Chittorgarh, this breed is recognized for its long ears and adaptability to hilly terrain.
- Nali: This breed is found in Hanumangarh and Shri Ganganagar, mainly along the Ghaggar river. Nali sheep are hardy animals that can thrive in semi-arid conditions.
- Pugal: Predominantly raised in Bikaner, Pugal sheep are known for their adaptability and contribution to the local wool industry.
- Magra: Also from Bikaner, the Magra breed is another important source of wool and is locally known as Bikaneri Chokla.
- Marwari and Kheri: Found in Jodhpur, Barmer, and Nagaur, this breed is the most populous sheep breed in Rajasthan, making it a key contributor to wool production.
- Jaisalmeri: Raised in Jaisalmer and Jodhpur, this breed provides the highest quantity of wool among sheep breeds in Rajasthan, making it an important breed for the textile industry.
Foreign Sheep Breeds in Rajasthan
In addition to indigenous breeds, foreign breeds of sheep have been introduced to Rajasthan to improve wool quality and increase production:
- Russian Marino: Found in Tonk, Jaipur, and Sikar, this breed is primarily raised for its high-quality wool.
- Rambull: Found in Tonk, the Rambull breed is known for its resilience and wool production.
- Dorset: Also located in Tonk, this breed has been introduced for both wool and meat production.
- Corriedale: Raised in Chittorgarh, the Corriedale breed is known for its fine wool and meat production capabilities.
A map of Rajasthan, depicted below, highlights the regional distribution of these sheep breeds across the state.
Camel Breeds in Rajasthan
Camels are often referred to as the “ships of the desert,” and Rajasthan, with its vast arid regions, is home to some of the finest camel breeds in India. Jaisalmer is the district with the maximum camel population in Rajasthan. Camels are primarily raised for transportation, milk, and agricultural purposes.
Key Camel Breeds in Rajasthan
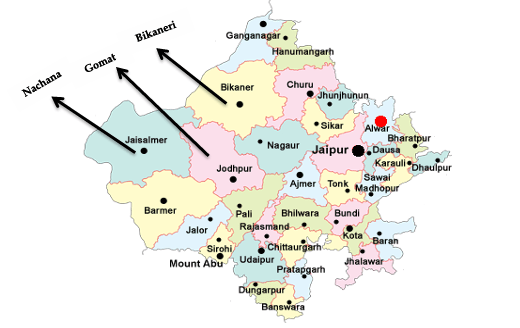
- Bikaneri: As the name suggests, this breed is native to Bikaner. The Bikaneri camel is known for its strength and stamina, making it ideal for carrying heavy loads. These camels are often used for transportation and agricultural work.
- Nachana: Raised in Jaisalmer, the Nachana breed is famed for its running speed and beauty. It is one of the best breeds for camel races and other cultural activities where camels play a central role.
- Gomat: Indigenous to Jodhpur, the Gomat breed is primarily raised for camel riding and is known for its elegance and endurance.
Other prominent breeds include the Sindhi, Kachhi, and Mewati camels, which are also raised for agricultural purposes and transport in various parts of Rajasthan.
Cultural and Economic Significance
Camels are not just beasts of burden in Rajasthan; they also hold immense cultural significance, especially in the Pushkar Camel Fair, one of the largest livestock fairs in the world. The Bikaneri camel is particularly showcased in this fair, where its physical attributes and strength are prized.
Camel Breeds in Rajasthan
| Breed | Area | Special Features |
| Bikaneri | Bikaner | Useful for carrying loads |
| Nachana | Jaisalmer | Best breed for running and beauty |
| Gomat | Jodhpur | Famous for camel riding |
| Sindhi | Western Rajasthan | Well adapted to arid conditions |
| Kachhi | Jaisalmer | Suitable for transport |
| Mewati | Alwar, Bharatpur | Useful in agriculture and travel |
Horses in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is known for its robust breeds of horses, particularly in Bikaner. Horses have traditionally played an important role in the region, especially for military and agricultural purposes. The following are the key horse breeds found in Rajasthan:
Key Horse Breeds
- Malani: This breed originates from Barmer and is regarded as one of the best horse breeds in Rajasthan. Malani horses are known for their strength and endurance, making them ideal for both military and agricultural uses.
- Marwari: Indigenous to Western Rajasthan, the Marwari horse is one of the most famous Indian horse breeds. It is renowned for its loyalty and bravery, historically serving in battles. The breed is also known for its unique inward-turning ear tips.
- Kathiyawari: Found in Barmer and Jalore, the Kathiyawari horse is another prestigious breed. It shares many similarities with the Marwari horse, especially in terms of its head structure, which resembles the Arabic horse.
The map of Rajasthan, provided below, highlights the geographic distribution of these horse breeds.
Distribution of Horse Breeds in Rajasthan
| Animal/Breed | Maximum Region | Area | Features |
| Malani (Horse) | Bikaner | Barmer | Best Breed of Horse |
| Marwari (Horse) | Bikaner | Western Rajasthan | Best Breed of Horse |
| Kathiyawari (Horse) | Bikaner | Barmer, Jalore | Head of this breed’s horse is similar to Arabic Horse |
| Donkey | Barmer | – | – |
| Hens | Ajmer, Udaipur | – | – |
| Pig | Jaipur, Bharatpur | – | – |
| Mule | Alwar | – | – |
Famous Animal Fairs of Rajasthan
Rajasthan hosts several significant animal fairs where livestock, including cattle, camels, and horses, are traded and showcased. These fairs are not only important for economic exchange but also for preserving cultural heritage. Below is a list of some of the most famous animal fairs in Rajasthan:
Famous Animal Fairs in Rajasthan
| Animal Fair | Place | Cattle Breed |
| Sri Baldev Cattle Fair | Medta (Nagaur) | Naguri |
| Shri Tejaji Cattle Fair | Nagaur | Naguri |
| Shri Ramdev Cattle Fair | Manasar (Nagaur) | Naguri |
| Shri Mallinath Cattle Fair | Tilwada (Barmer) | Tharparkar Kankrej |
| Chandra Bhaga Cattle Fair | Jhalarapatan (Jhalawar) | Malvi |
| Shri Gomtisagar Cattle Fair | Jhalarapatan (Jhalawar) | Malvi |
| Jaswant Cattle Fair | Bharatpur | Haryanvi |
| Gogamedi Cattle Fair | Hanumangarh | Haryanvi |
| Shivratri Cattle Fair | Karauli | Haryanvi |
| Kartik Cattle Fair | Pushkar | Gir / Ajmera / Renda |
Animal Breeding and Research Centers in Rajasthan
Rajasthan has several key centers dedicated to the research and development of livestock breeds. These centers are crucial in improving livestock productivity, ensuring genetic diversity, and promoting sustainable livestock management practices.
Animal Breeding and Research Centers in Rajasthan
| Breeding and Research Center | Location |
| National Research Center on Camel | Jodbeed (Bikaner) |
| Central Animal Research Center | Suratgarh (Ganganagar) |
| Sheep and Wool Research Center | Avikanagar (Tonk) |
| Buffalo Research Center | Vallabh Nagar (Udaipur) |
| Buffalo Breeding Center | Dag (Jhalawar), Kumher (Bharatpur) |
| Bull Mother Farm | Chandan Village (Jaisalmer) |
| Goat Breeding Center | Ramsar (Ajmer) |
| Pig Breeding Center | Alwar |
| Horse Breeding and Research Institute | Keru (Jodhpur) |
These centers are essential for Rajasthan’s rural economy, focusing on genetic research, breed improvement, and animal health. The National Research Center on Camel in Bikaner is particularly notable for its work on camel breeding and management.
Major Schemes and Institutes for Animal Development
Several schemes and institutes in Rajasthan focus on the development and breeding of livestock, with the objective of increasing productivity and providing employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Gopal Scheme
- Started: 2nd October, 1990
- Objective: To improve the breeds of animals by involving rural youth in economic development through livestock rearing. The scheme also focuses on providing employment opportunities to rural youth by increasing livestock productivity.
- Kaamdhenu Scheme
- Started: 1997-1998
- Objective: This scheme focuses on establishing animal breeding farms based on bovine-related techniques. It aims to enhance cattle breeds and boost milk production through advanced breeding methods.
Major Schemes for Animal Development in Rajasthan
- ADMAS (Animal Diseases Monitoring and Surveillance) Scheme
- Started: 1999
- Objective: This scheme aims to ensure that cow and buffalo breeds are free from diseases. This is achieved through the efforts of the Indian Council for Agricultural Research (ICAR), focusing on disease monitoring and surveillance.
- Rajiv Gandhi Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Development
- Started: 19th January 2010
- Objective: To fulfill the objectives set out in the Animal Development Policy, which include improving livestock breeds and enhancing animal husbandry practices to support the rural economy.
- Mukhyamantri Livestock Free Drug Scheme
- Started: 15th August 2012
- Objective: Under this scheme, essential medicines are provided free of cost for animal healthcare by the state government, aiming to improve livestock health and productivity.
- Avika Kavach Yojana
- Started: 2004, with updates in 2009 and 2018
- Objective: Aimed specifically at sheep insurance, this scheme provides an 80% subsidy on the insurance premium for SC/ST and BPL categories. Other livestock breeders receive a 70% subsidy. This initiative helps protect the income of shepherds by insuring their livestock.
- Bhamashah Animal Insurance Scheme
- Objective: This scheme insures various livestock animals for a duration of either one or three years. A 70% subsidy is provided to BPL, SC, ST categories, and 50% to the remaining cattle rearers.
- Sum Insured:
- Cow: ₹40,000
- Buffalo: ₹50,000
- Sheep/Goat/Pig (10 units): ₹50,000
- Camel/Horse/Donkey: ₹50,000
- Each family can insure up to 5 large animals and 50 small animals.
Important Facts
- Ibomix: This is a chemical mixture developed by CAZARI scientists. It is used to improve milk production in goats and sheep. When mixed with water, Ibomix helps stimulate milk production, thereby benefiting the dairy industry in Rajasthan.
- Cow Buffalo Breeding Policy: Introduced in 2014-15, this policy aims at enhancing cattle breeds through scientifically guided breeding programs, thereby increasing milk yield and improving livestock quality.
- Rajasthan Animal Development Board: Established on 25th March 1998 in Jaipur, the board plays a key role in coordinating animal husbandry activities and promoting livestock development across the state.
- Rajasthan University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences: Located in Bikaner, this university offers education and research in animal sciences, helping advance the knowledge and techniques required for sustainable livestock management.
- Himkart Veerya Bank: Established in Bassi, Jaipur on 14th August 2007, this facility focuses on preserving genetic material for breeding and animal development purposes.
- Cow Urine Refinery: Located in Pathmeda, Jalore, this refinery processes cow urine for medicinal purposes, demonstrating Rajasthan’s innovative approach to animal byproducts.
These schemes and innovations demonstrate Rajasthan’s commitment to improving its livestock economy through insurance, scientific advancements, and sustainable animal husbandry practices.


