Unraveling The Wonders Of Literature In Ancient India: A Journey Through Time
Unraveling the Wonders of Literature in Ancient India: A Journey Through Time
Introduction
Welcome to the mesmerizing realm of Literature in Ancient India, where tales of valor, wisdom, and spirituality intertwine to create a tapestry of cultural heritage.
From the Rigveda, the oldest known text in the world, to the timeless epics of the Mahabharata and Ramayana, the literary landscape of ancient India is as vast and diverse as the subcontinent itself.
In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries and marvels of ancient Indian literature, exploring its origins, genres, and enduring influence on the world.
Exploring the Origins of Literature in Ancient India
The Vedic Period
The Vedic Period, spanning from around 1500 BCE to 500 BCE, marked the genesis of Indian literary tradition. It was characterized by the composition of the Rigveda, a collection of hymns dedicated to various deities.
These sacred texts not only provided insights into early Indian society, religious beliefs, and philosophical concepts but also served as a cornerstone for subsequent literary developments.
Epics and Puranas
The epic literature of ancient India, including the Mahabharata and Ramayana, holds a special place in Indian culture and spirituality. Composed over centuries, these epic narratives are not just stories but profound reflections on human nature, morality, and the cosmic order.
The Mahabharata, with its complex characters and intricate plotlines, explores themes of duty, righteousness, and the consequences of human actions. Similarly, the Ramayana, depicting the life and adventures of Lord Rama, exemplifies ideals of honor, loyalty, and sacrifice.
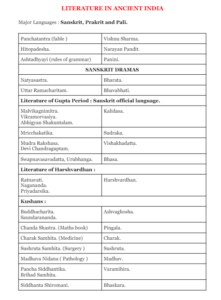
Sanskrit Literature
The classical period of ancient India, from around 500 BCE to 1000 CE, witnessed a flourishing of Sanskrit literature. This period produced some of the most enduring works of Indian literature, ranging from sublime poetry to philosophical treatises.
One of the greatest poets of this era was Kalidasa, renowned for his lyrical compositions such as the Meghaduta and Shakuntala. Sanskrit literature also encompassed a wide range of genres, including epic poetry (Mahakavya), drama (Nataka), and prose (Katha).
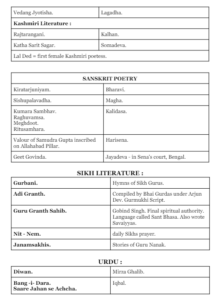
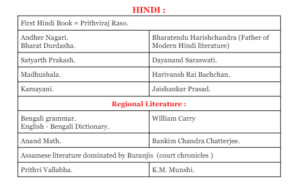
Regional Literature
While Sanskrit was the language of the elite, ancient India was also home to a vibrant tradition of regional literature. Tamil Sangam literature, dating back to the early centuries CE, is a testament to the rich cultural heritage of South India. These Sangam poems, composed by various poets, celebrate love, nature, and the fleeting beauty of life.
Similarly, Kannada vachana poetry, rooted in the Bhakti movement, expressed devotion to the divine in simple yet profound verses. Bengali medieval literature, influenced by Vaishnavism and Sufism, produced timeless works such as the Charyapada and Mangal-Kavyas.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| The Vedic Period | The Vedic Period witnessed the composition of the Rigveda, providing insights into early Indian society and religious beliefs. |
| Epics and Puranas | Epic literature, including the Mahabharata and Ramayana, explored profound themes of duty, righteousness, and cosmic order. |
| Sanskrit Literature | Sanskrit literature flourished during the classical period, producing sublime poetry, philosophical treatises, and dramatic works. |
| Regional Literature | Regional languages such as Tamil, Kannada, and Bengali contributed to a diverse literary landscape, showcasing unique cultural expressions and traditions. |
The Significance of Literature in Ancient India
Preservation of Knowledge
Ancient Indian texts served as repositories of knowledge, encompassing diverse fields such as philosophy, science, medicine, and ethics. Through meticulous oral transmission and later written records, this knowledge was preserved and passed down through the ages.
Spiritual and Philosophical Insights
Many ancient Indian texts, such as the Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita, delve into profound philosophical inquiries about the nature of existence, the self, and the universe. These timeless teachings continue to inspire seekers on the path of spiritual enlightenment.
Cultural Identity and Heritage
Literature in Ancient India reflects the cultural identity and heritage of the Indian subcontinent, celebrating its linguistic diversity, artistic expressions, and societal values. It serves as a source of pride and inspiration for millions around the world.
Literary Techniques and Aesthetics
Ancient Indian literature exhibits a mastery of literary techniques and aesthetics, including intricate poetic meters, vivid imagery, and allegorical storytelling. These artistic flourishes enhance the beauty and impact of the texts, captivating readers across generations.
FAQs
What is the significance of the Mahabharata and Ramayana in ancient Indian literature?
The Mahabharata and Ramayana are epic narratives that embody the moral and ethical values of ancient Indian society. They explore themes of duty, honor, and divine intervention, offering timeless lessons for humanity.
How did Sanskrit literature contribute to the cultural heritage of ancient India?
Sanskrit literature encompasses a wide range of genres, including poetry, drama, and philosophy. It played a pivotal role in shaping the intellectual and spiritual landscape of ancient India, influencing subsequent generations of scholars and thinkers.
What role did oral tradition play in the transmission of ancient Indian texts?
Oral tradition was integral to the preservation and dissemination of ancient Indian texts, especially during the Vedic period. Skilled reciters known as sutas memorized and chanted the sacred hymns, ensuring their transmission from one generation to the next.
How did regional literature contribute to the diversity of literary expression in ancient India?
Regional literature in languages such as Tamil, Kannada, and Bengali showcased the linguistic and cultural diversity of ancient India. It provided a platform for local poets and scholars to express their unique perspectives and experiences.
What are some notable examples of philosophical texts in ancient Indian literature?
The Upanishads, Vedanta Sutras, and Bhagavad Gita are among the most renowned philosophical texts in ancient Indian literature. They explore profound metaphysical concepts such as the nature of reality, the self, and the ultimate goal of human life.
How has ancient Indian literature influenced modern literature and culture?
The themes, motifs, and moral lessons found in ancient Indian literature continue to resonate in modern literature, cinema, and performing arts. From adaptations of the epics to contemporary reinterpretations of classical texts, the legacy of ancient Indian literature endures in diverse forms of artistic expression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, literature in Ancient India is a treasure trove of wisdom, beauty, and cultural heritage that continues to captivate and inspire audiences worldwide.
From the timeless epics of the Mahabharata and Ramayana to the profound philosophical insights of the Upanishads, the legacy of ancient Indian literature transcends the boundaries of time and space.
By exploring the origins, significance, and enduring influence of ancient Indian texts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of human creativity and spirituality.