United Nations Security Council (UNSC)

- The UNSC is one of the six principal organs of the UN, established by the UN Charter in 1945.(The other 5 organs of the United Nations are—the General Assembly (UNGA), the Trusteeship Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat).
- Headquarter – New York, USA
- It has the primary responsibility for maintaining international peace and security and can issue legally binding resolutions on all UN member states.
- It consists of 15 members: five permanent members (China, France, Russia, UK, and US) and 10 non-permanent members elected by the UNGA for two-year terms.
- Each year, the General Assembly elects five non-permanent members (out of ten in total) for a two-year term. The ten non-permanent seats are distributed on a regional basis.
- The council’s presidency is a capacity that rotates every month among its 15 members in the English alphabetical order of the member states’ names.
- The permanent members have the power to veto any substantive resolution, which has been a source of criticism and controversy.
- The UNSC also plays a role in admitting new members to the UN, recommending candidates for the office of Secretary-General, and approving amendments to the UN Charter.
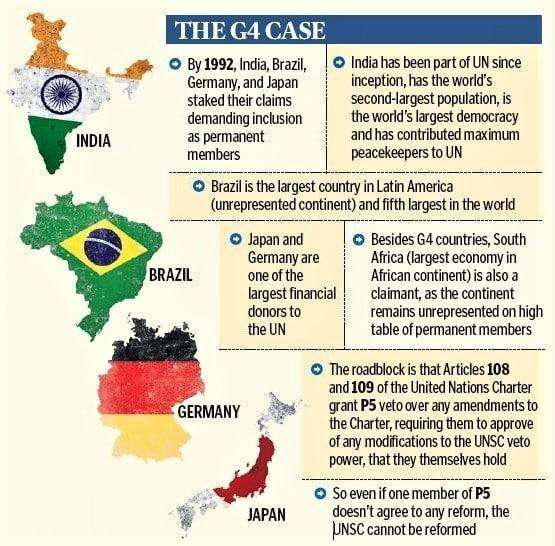
- India has been a non-permanent member of the UNSC eight times, the latest being 2021-22. India has also been campaigning for a permanent seat in the UNSC, along with Brazil, Germany, and Japan (the G4 group).
- Absence of Records and Texts of Meetings:
The usual UN rules don’t apply to the UNSC deliberations and no records are kept of its meetings. Additionally, there is no “text” of the meeting to discuss, amend or object.
- The UNSC has established more than 70 peacekeeping operations since 1948, involving more than one million peacekeepers from over 120 countries. India is one of the largest troop-contributing countries (Rank Third, after Bangladesh and Nepal), with a history of deploying soldiers, medical personnel, and engineers to various peacekeeping missions worldwide.
- The UNSC has also imposed sanctions on countries or groups that threaten international peace and security, such as Iran, North Korea, Libya, Sudan, Somalia, and the Taliban. Sanctions can include arms embargoes, travel bans, asset freezes, and trade restrictions.
- The UNSC has adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948, which is the first document to detail the fundamental human rights that must be protected. The UNSC also oversees the work of the UN Human Rights Council and other human rights bodies.
- The UNSC has played a key role in addressing global challenges such as climate change, nuclear proliferation, terrorism, and pandemics. For example, the UNSC endorsed the Paris Agreement on climate change in 2016, which was signed by the largest number of countries ever in a single day.
Voting Powers:
- Each member of the Security Council has one vote.
- Decisions of the Security Council on matters are made by an affirmative vote of nine members including the concurring votes of the permanent members. A “No” vote from one of the five permanent members blocks the passage of the resolution (called ‘Veto’).
- Any member of the United Nations which is not a member of the Security Council may participate, without vote, in the discussion of any question brought before the Security Council whenever the latter considers that the interests of that member are specially affected.
G4 v/s Coffee Club
- Uniting for Consensus (UfC), nicknamed the Coffee Club, is a movement that developed in the 1990s in opposition to the possible expansion of permanent seats in the United Nations Security Council.
- Under the leadership of Italy, it aims to counter the bids for permanent seats proposed by G4 nations (Brazil, Germany, India, and Japan) and is calling for a consensus before any decision is reached on the form and size of the United Nation Security Council.
- Italy, through the ambassador Francesco Paolo Fulci, along with Pakistan, Mexico and Egypt, founded the “Coffee Club” in 1995.
- The prime movers of the club include Italy, Spain, Australia, Canada, South Korea, Argentina, and Pakistan.

